Le Léman au printemps
Réchauffement et redémarrage du développement algal
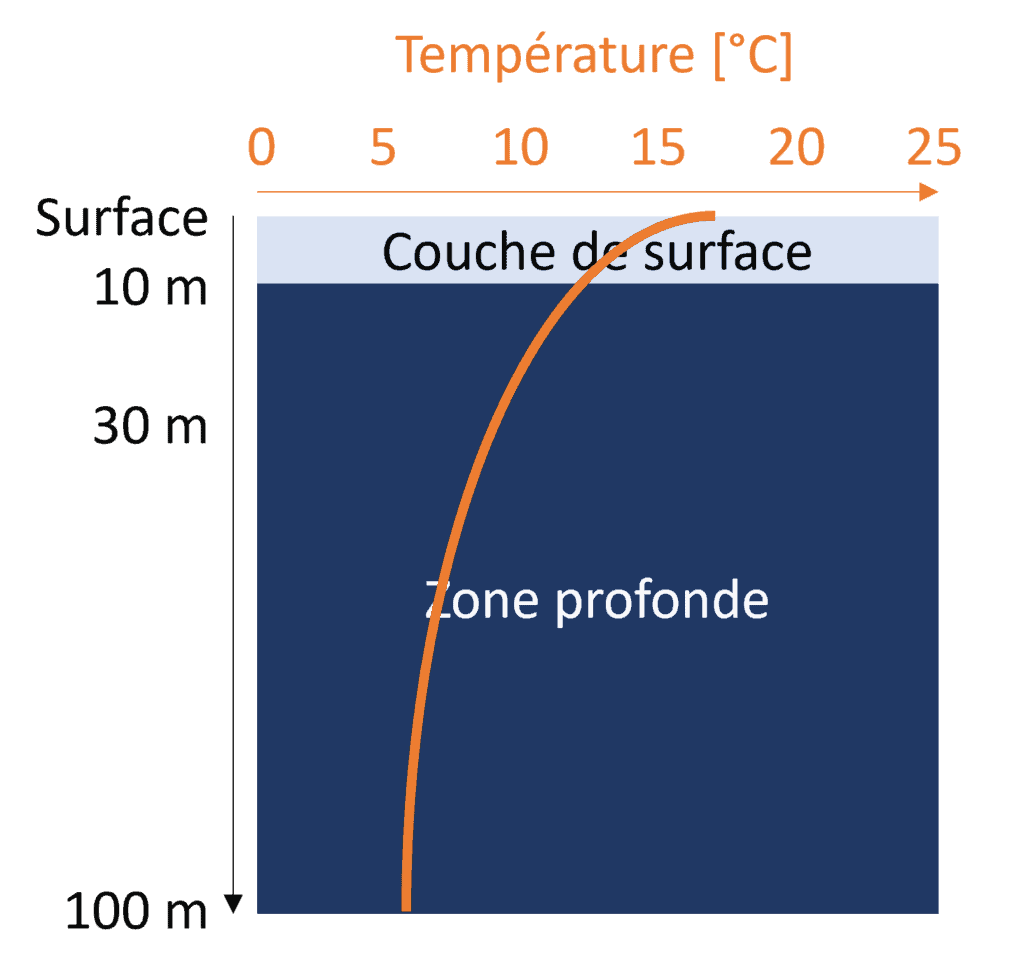
Au printemps, les campagnes de mesure de qualité des eaux du lac redeviennent bimensuelles pour suivre au mieux le réchauffement des eaux et le redémarrage du développement des algues en suspension dans l’eau.
Le brassage hivernal a entraîné la remobilisation en surface des nutriments nécessaires au développement des algues (azote et phosphore principalement). Le réchauffement printanier, combiné à l’augmentation du rayonnement solaire, permet le redémarrage du développement des algues dans la couche de surface riche en nutriments. Le redémarrage du développement des algues s’accompagne d’une baisse de la transparence des eaux de surface.
Les algues sont importantes pour le fonctionnement du lac car elles constituent la base de la chaîne alimentaire. La majorité d’entre elles ne pose pas de problème, mais certaines espèces sont problématiques : celles qui colmatent les filets de pêche, et les cyanobactéries toxiques.